Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis and Its Blood Test
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide, yet remains largely misunderstood. When a blood clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs, it can pose serious health risks, including the potential to lead to pulmonary embolism. This article will explore the intricacies of deep vein thrombosis, its symptoms, risk factors, the crucial blood test involved, and how professionals at Truffles Vein Specialists can assist in diagnosis and treatment.
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs. The condition is serious because the clot can break loose and travel to the lungs, causing a potentially fatal pulmonary embolism. Understanding DVT is essential for recognizing the symptoms and seeking appropriate medical care.
Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Identifying DVT symptoms early can be crucial. Common symptoms include:
- Swelling: Often occurring in one leg, it may be accompanied by a feeling of heaviness.
- Pain: A cramping or soreness that typically starts in the calf and may feel like a charley horse.
- Red or discolored skin: The affected area may appear reddish or bluish.
- Warmth: The skin over the affected area may feel warm to the touch.
Many people with DVT experience only mild symptoms, or even none at all. Hence, it's crucial to consult a medical professional if you suspect you may have this condition.
Risk Factors for Developing Deep Vein Thrombosis
Several factors can increase your risk of developing DVT:
- Prolonged inactivity: Long periods of sitting, particularly during travel (like long flights), can lead to blood clot formation.
- Medical history: A history of DVT or certain conditions that affect blood clotting increases risk.
- Age: The risk of DVT increases with age, particularly after age 60.
- Obesity: Excess weight adds pressure to veins in the pelvis and legs.
- Smoking: Tobacco use can damage blood vessels and enhance clotting risks.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can increase clotting factors.
Awareness of these risk factors is essential for both prevention and early intervention. If you identify with any of these risk factors, consider discussing your concerns with a healthcare provider.
The Importance of the Deep Vein Thrombosis Blood Test
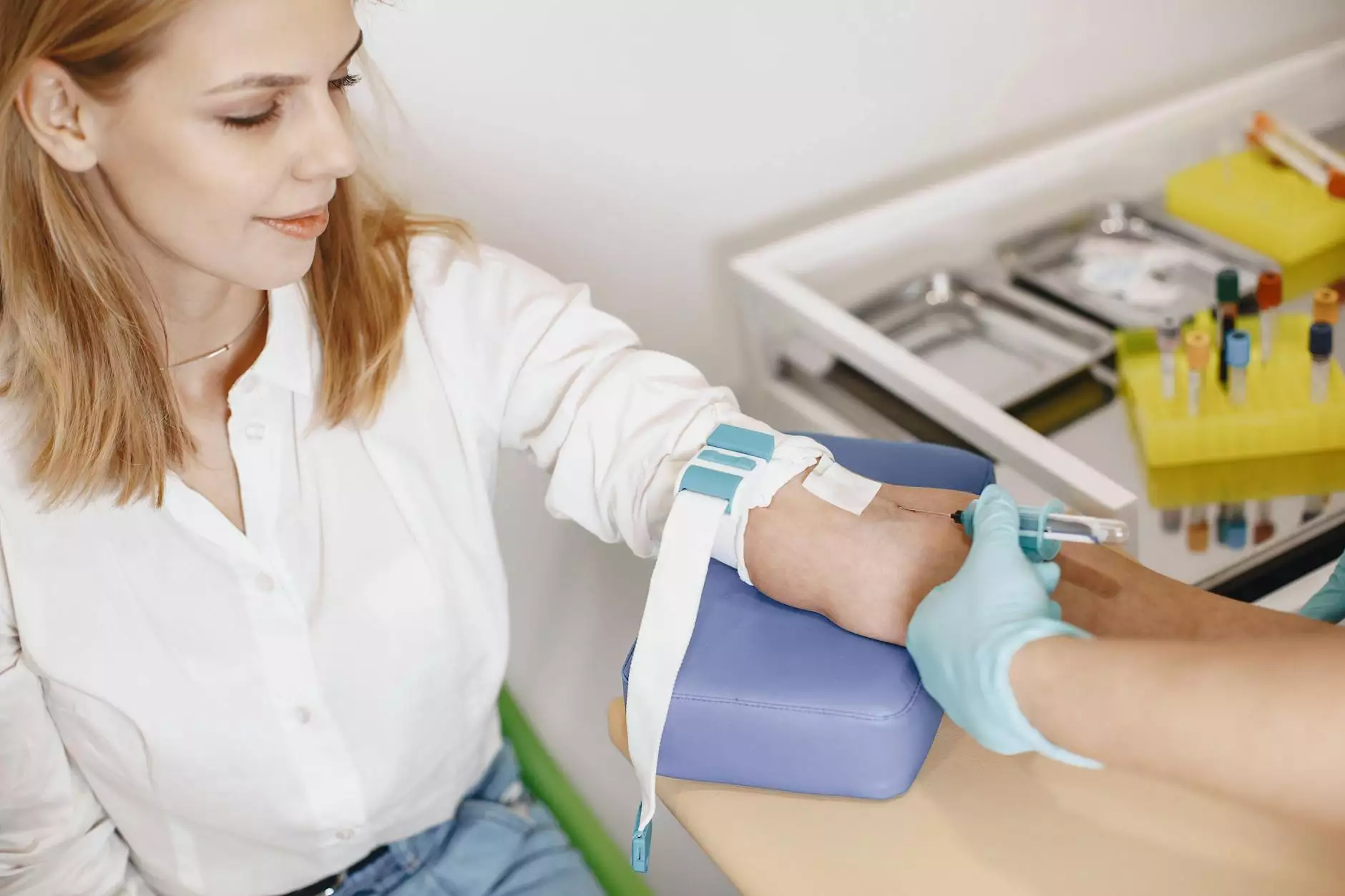
When DVT is suspected, medical professionals often recommend a deep vein thrombosis blood test. This diagnostic tool helps determine the presence of blood clots in the body. The most widely used test for this purpose is the D-dimer test.
What is a D-dimer Test?
The D-dimer test measures the level of D-dimer, a protein fragment produced when a blood clot dissolves. Elevated levels of D-dimer could indicate the presence of an abnormal blood clot, leading to further investigation.
How D-dimer Testing Works
The test involves taking a small sample of blood from a vein, which is then analyzed in a laboratory. Here’s how to approach it:
- Preparation: No special preparation is usually needed before the test, although you should consult with your doctor regarding any medications you are taking.
- Blood sample collection: A healthcare professional will clean the area where the needle will be inserted, then draw a small amount of blood.
- Analysis: The blood sample is sent to a lab for evaluation. Results are typically available within a few hours to a day.
Interpreting D-dimer Test Results
It's important to note that while elevated D-dimer levels can indicate DVT, other conditions can also raise these levels, such as infection or recent surgery. Thus, a high D-dimer result does not necessarily confirm a diagnosis of DVT. Follow-up imaging tests, such as Doppler ultrasound, are often needed to confirm the presence of a clot.
Diagnosing Deep Vein Thrombosis: The Role of Imaging Tests
In conjunction with blood tests, imaging plays a critical role in diagnosing DVT. Common imaging tests include:
- Doppler ultrasound: This non-invasive test uses sound waves to create an image of blood flow in the veins. It’s the most commonly used method for diagnosing DVT.
- CT or MRI scans: These imaging tests may be used if DVT is suspected in less accessible areas of the body or if there are complications.
For accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment, advancing diagnostic techniques allow healthcare professionals to develop an effective treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Deep Vein Thrombosis
The treatment for DVT primarily focuses on preventing the clot from growing and reducing the risk of pulmonary embolism. Here are the main treatment options:
- Anticoagulants: Also known as blood thinners, these medications help prevent new clots from forming and allow existing clots to dissolve.
- Compression stockings: These specialized stockings help prevent swelling and reduce the likelihood of DVT recurrence.
- Thrombolytics: In severe cases, thrombolytic medications may be used to dissolve large clots quickly.
- Inferior vena cava filter: This device can be implanted in the inferior vena cava (the large vein that carries blood from the lower body to the heart) to prevent clots from reaching the lungs.
The Importance of Follow-Up Care
After treatment, ongoing follow-up care is essential. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers such as those at Truffles Vein Specialists can help ensure that your condition is monitored and managed effectively.
Prevention Strategies for Deep Vein Thrombosis
Preventing DVT is crucial, especially for individuals at higher risk. Here are some effective strategies for prevention:
- Stay active: Engage in regular physical activity, especially if your job or lifestyle involves prolonged periods of inactivity.
- Wear loose clothing: Comfortable clothing can improve circulation.
- Maintain a healthy weight: A balanced diet and regular exercise can help manage weight and reduce pressure on the veins.
- Avoid tobacco: Quitting smoking can improve vascular health and reduce the chances of developing DVT.
- Stay hydrated: Adequate hydration supports healthy circulation.
- Consider medication if traveling: For long journeys, consult your doctor about preventive measures such as wearing compression stockings or taking anticoagulants.
Conclusion: Take Charge of Your Vascular Health
Deep vein thrombosis is a serious condition, but with awareness and proactive measures, you can significantly reduce your risk. Regular check-ups and blood tests are essential components of this effort. If you're concerned about DVT or need a deep vein thrombosis blood test, don’t hesitate to contact Truffles Vein Specialists. Our team of experts is dedicated to helping you understand your vascular health and providing the highest standard of care.
Your health is your wealth, and being informed is the first step towards a healthier life. Don't wait—take your first step today by seeking professional advice and getting the support you need!



